Agile project management is essential for teams that need to adapt quickly, deliver in increments, and collaborate effectively. While tools like Jira and Trello have dominated the Agile landscape, Planner offers a robust and flexible alternative within the Microsoft ecosystem.
What is Microsoft Planner?
Microsoft Planner is a modern project management tool that offers a visual, web-based interface for tracking tasks, resources, and timelines.
It’s built on the Power Platform and is part of the Microsoft 365 suite, allowing seamless integration with Power BI, Planner and Teams for improved collaboration and reporting. While often linked to waterfall project management, it can also be adapted for Agile methodologies.
Managing an Agile project with Microsoft Planner
1. Choose your template
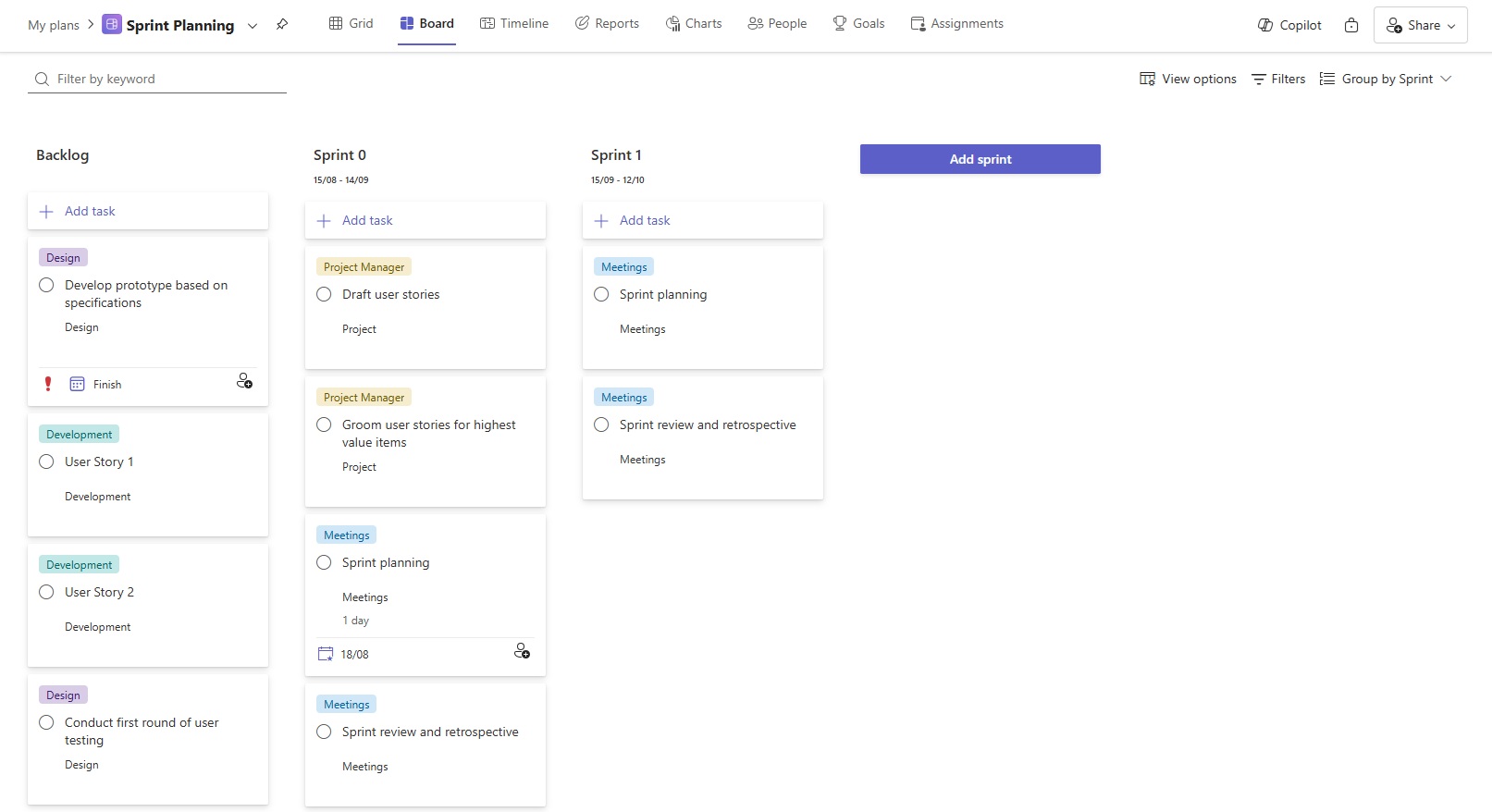
There are several project plan templates in Microsoft Planner that come with predefined tasks and timelines catering to common project types. There are two templates for managing Agile projects:
- Sprint Planning: Designed for Agile teams to organize and manage short, time-boxed sprints. Ideal for short-term planning and execution of features or bug fixes.
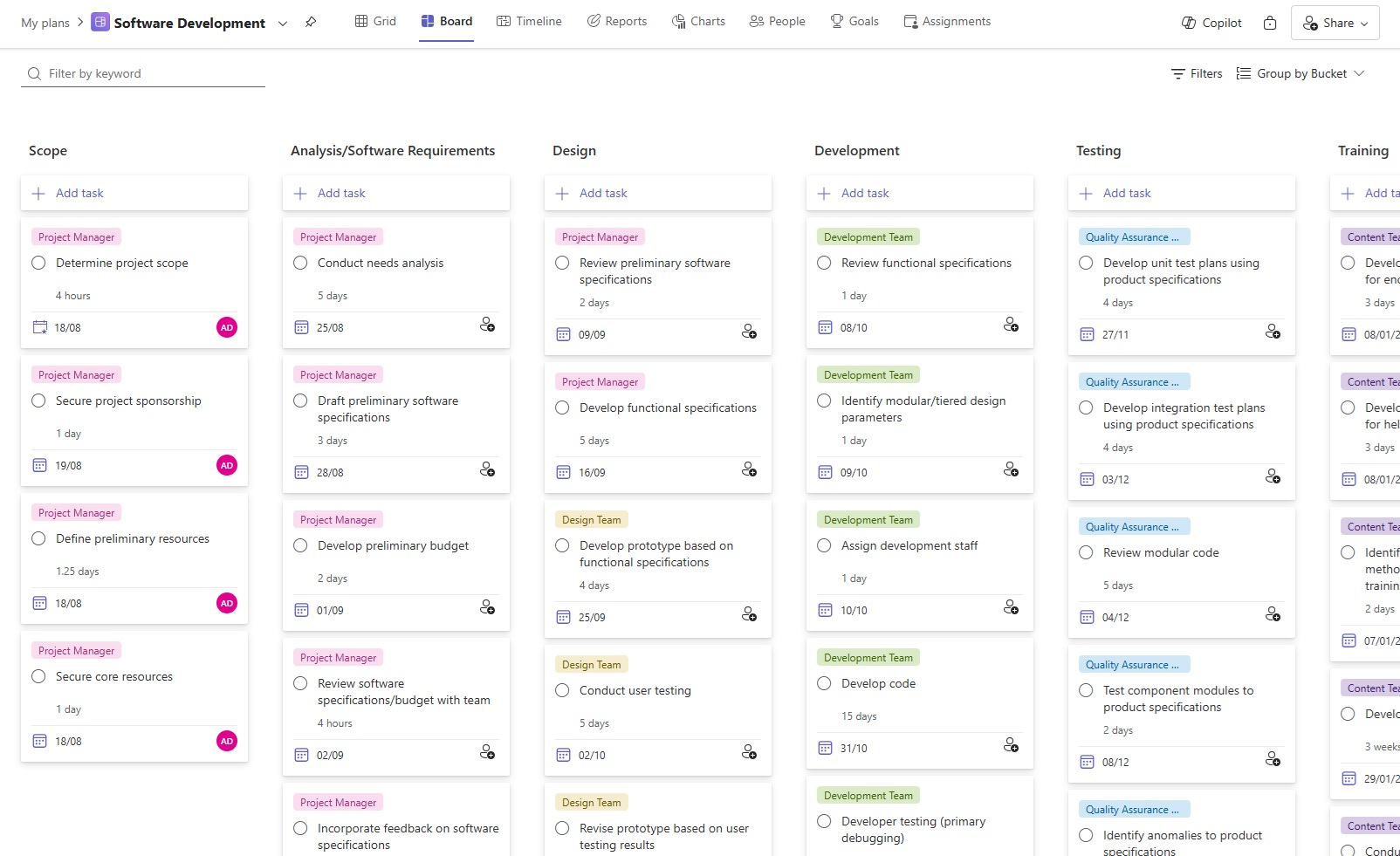
- Software Development: Covers the entire software project lifecycle, from feature development to release. Best for long-term planning, and tracking phases, milestones, and releases beyond individual sprints.
2. Use Kanban boards
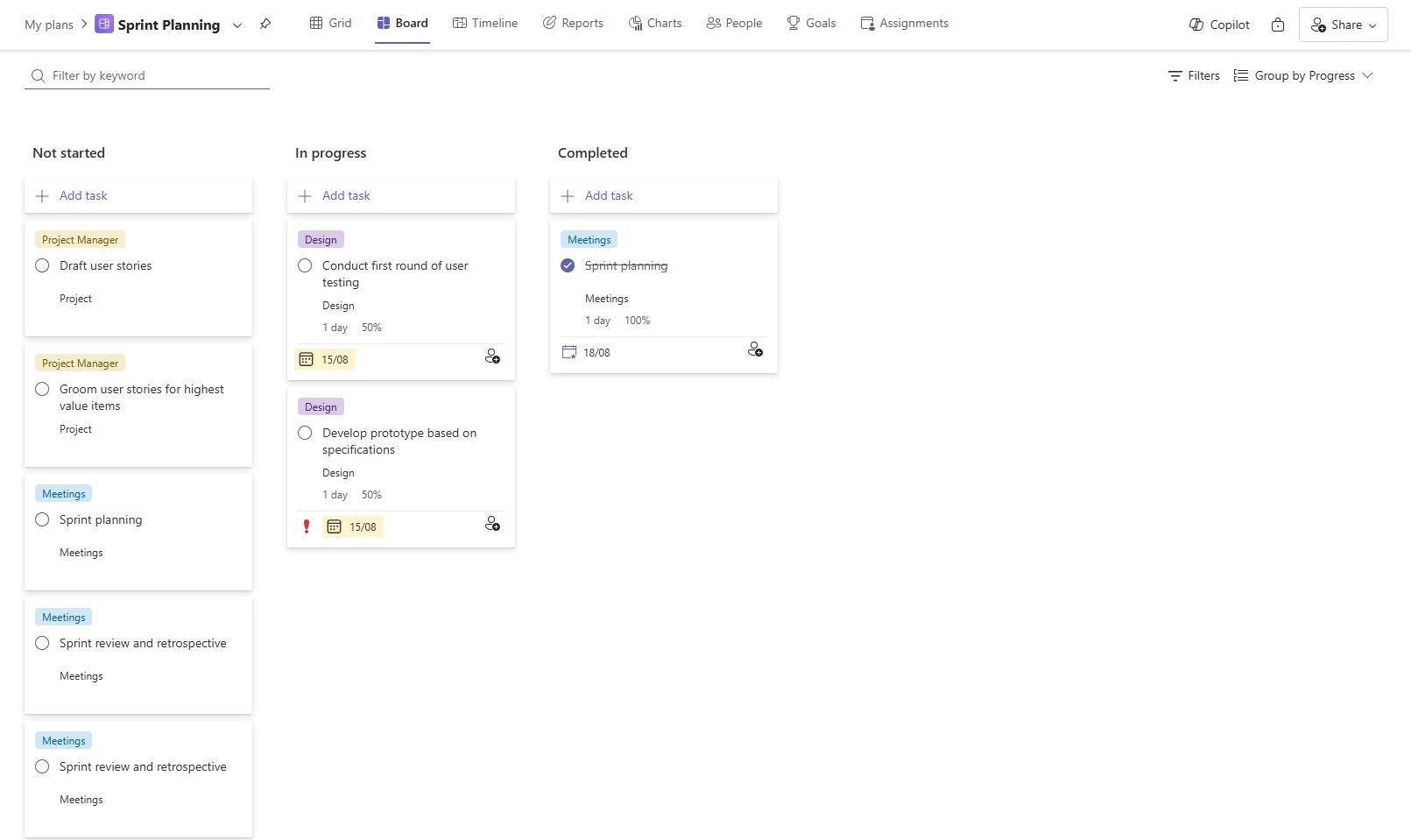
Planner offers three views — Grid, Timeline, and Board — to suit different project management styles. The Board view is especially useful for Agile teams, allowing for visual task management in a Kanban-style layout. Here are some key grouping options:
- Group by Progress: Automatically sorts tasks into categories like Not Started, In Progress, and Completed. Great for daily stand-ups.
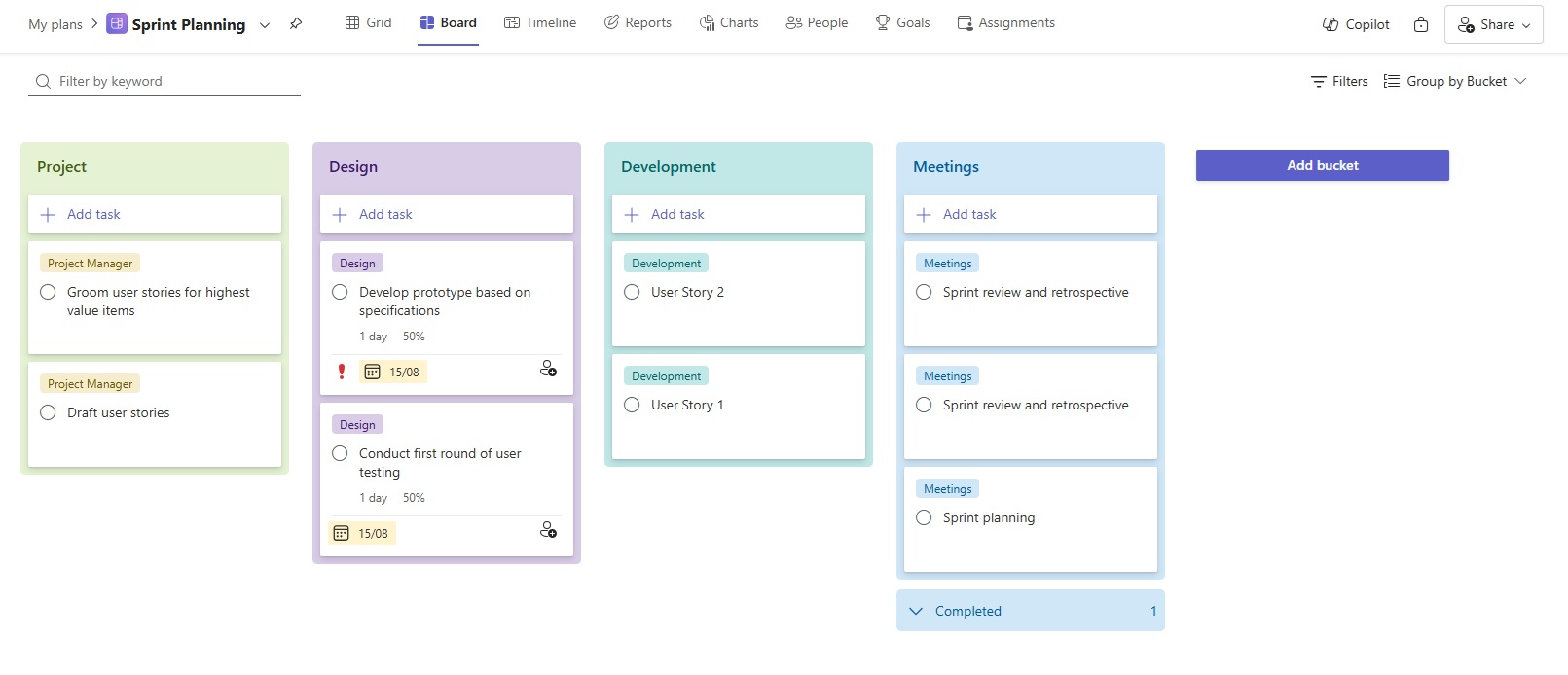
- Group by Bucket: Separates work into different phases or categories, helping with sprint planning and tracking progress across multiple sprints.
- Group by Sprint: Clearly organizes tasks by their assigned sprint, making it ideal for sprint reviews and monitoring velocity.

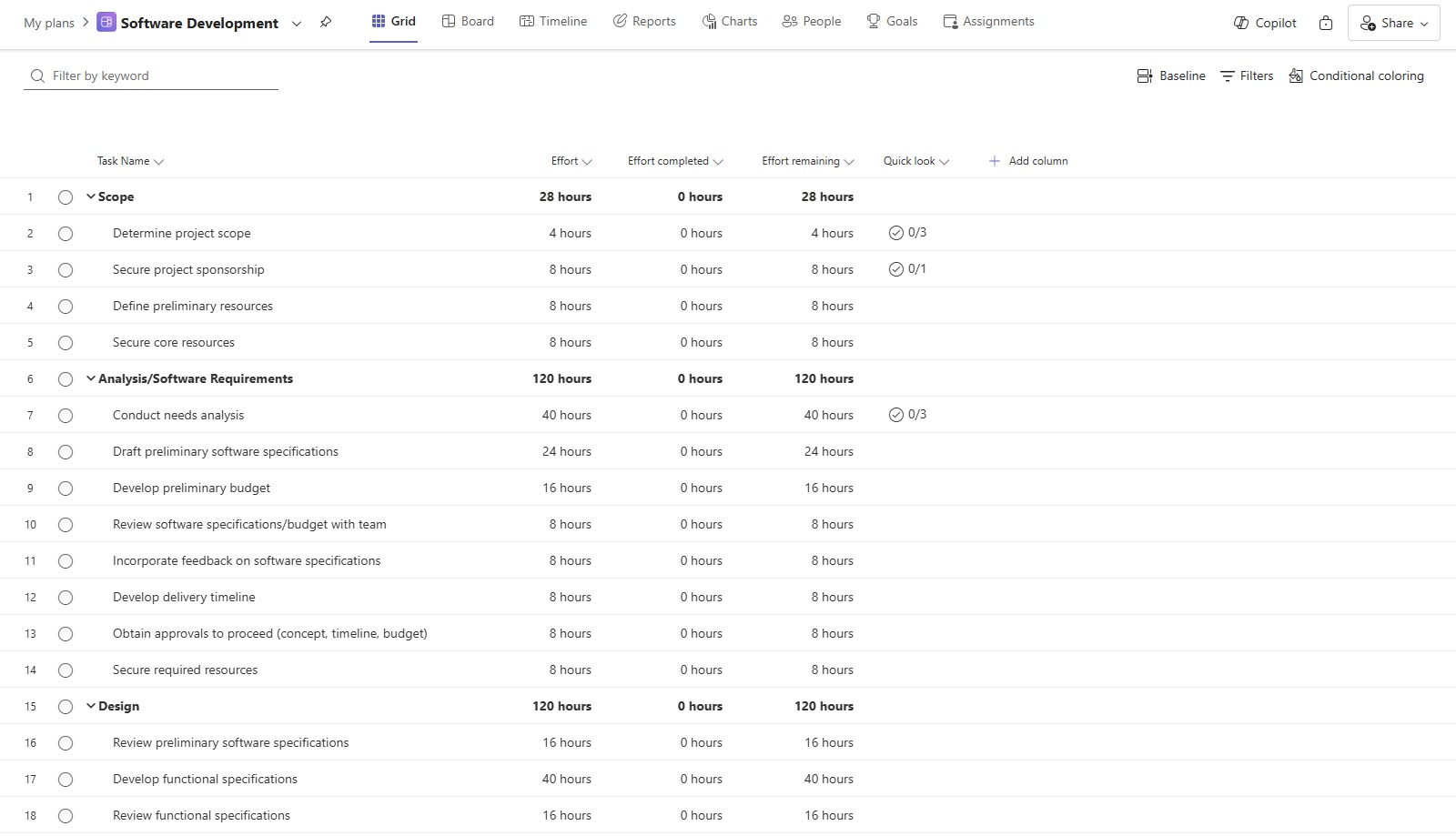
3. Track effort
By effectively tracking effort, Agile teams can enhance their planning, improve collaboration, and achieve better overall outcomes. Planner facilitates monitoring progress through three key fields:
- Effort: Total amount of work required to complete a task, usually measured in hours or days. Use this during sprint planning to determine how many tasks can realistically fit into a sprint, ensuring the team is not overcommitted.
- Effort completed: Amount of work that has already been completed on a task. Use this field in daily stand-ups to provide quick updates on what’s been achieved and what still needs attention.
- Effort remaining: Amount of work still needed to complete a task. Discuss this during sprint reviews to evaluate what can realistically be completed in the remaining time and adjust plans if necessary.
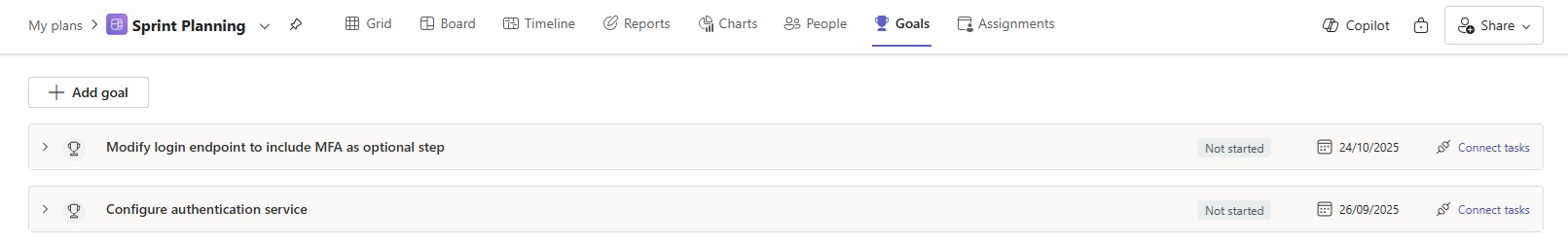
4. Set sprint goals
Sprint goals give teams a clear objective, helping everyone understand what needs to be achieved. They help prioritize tasks so team members can focus on what’s most important and avoid distractions.
At the start of a sprint, use the Goals tab to set clear goals and link them to specific tasks. This ensures everyone knows how their work contributes to the overall project objectives, boosting motivation and focus.
While Microsoft Planner web may not have been originally designed with Agile in mind, its flexibility and integration with other Microsoft tools make it a powerful solution for Agile project management.
By taking advantage of its Kanban boards and customizable workflows, your team can effectively manage sprints, track progress, and deliver high-quality results in an iterative, collaborative manner.
This post was previously published on Medium.com.

